- Home
- About ANT
-
Products
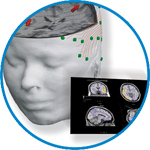
asa
asa is a highly flexible EEG/ERP and MEG analysis package with a variety of source reconstruction, signal analysis and MRI processing features.
.jpg)
eego mylab
The new frontier in multimodal brain research. With up to 16 kHz sampling rate, 256 EEG channels and unique software features, eego mylab gives you an unprecedented in-depth understanding of the human brain.

eego sports
eego sports offers complete freedom to collect high-density EEG data, bipolar EMG signals, and a variety of physiological sensor data, wherever and whenever required, with publish quality data in less than 15 minutes!

waveguard net
The waveguard net sets a new standard for research applications requiring high-density EEG data acquisition with quick preparation time, high flexibility, and subject comfort.
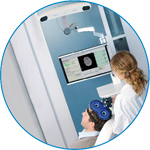
visor2
Our new and upgraded visor2 solutions integrate all the latest technologies for navigated rTMS, dual-coil navigation support, EEG-TMS recordings and pre-surgical evaluation for the highest quality in research and clinical procedures.
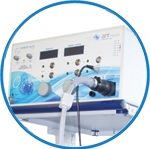
powerMAG ANT
The PowerMAG ANT 100 rTMS stimulator is designed for the specific needs of high-end TMS applications. Powerful high-frequency TMS as well as high precise single pulse and repetitive pulse protocols are combined in one single device.

xensor
xensor offers the solution for digitization of 3D electrode positions. xensor takes care of the whole procedure; it records, visualizes and stores positions acquired with a dedicated digitizer.

waveguard original
waveguard original is the cap solution for EEG measurements compatible with fMRI, MEG and TMS system. Use of active shielding guarantees performance in even the most demanding environments.
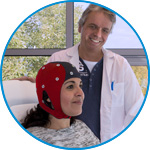
waveguard connect
waveguard connect EEG caps are a perfect match for hospitals and institutes aiming at reliable EEG, maximum uptime and great patient comfort! For optimal signal quality, the electrodes are made of pure, solid tin.

waveguard touch
waveguard touch is a dry electrode EEG cap. The unique Ag/AgCl coated soft polymer electrodes provide stable, research-grade EEG signals while maintaining subject comfort. The combination of these innovative dry electrodes and the industry-leading waveguard cap makes waveguard touch the best solution for dry EEG.
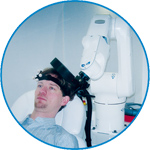
smartmove
smartmove allows planning of a complete TMS session ahead by defining stimulation sites based on anatomical MRI information and functional information like fMRI, PET or EEG/MEG.
Stay - References
- Support
- Events
- News
- Contact Us
You are here
A Comparative Study of Electrical Potential Sensors and Ag/AgCl Electrodes for Characterising Spontaneous and Event Related Electroencephalagram Signals
A Comparative Study of Electrical Potential Sensors and Ag/AgCl Electrodes for Characterising Spontaneous and Event Related Electroencephalagram Signals
Background
Electroencephalography (EEG) is still a widely used imaging tool that combines high temporal resolution with a relatively low cost. Ag/AgCl metal electrodes have been the gold standard for non-invasively monitoring electrical brain activity. Although reliable, these electrodes have multiple drawbacks: they suffer from noise, such as offset potential drift, and usability issues, for example, difficult skin preparation and cross-coupling of adjacent electrodes.
New Method
In order to tackle these issues a prototype Electric Potential Sensor (EPS) device based on an auto-zero operational amplifier was developed and evaluated. The EPS is a novel active ultrahigh impedance capacitively coupled sensor. The absence of 1/f noise makes the EPS ideal for use with signal frequencies of ∼10 Hz or less. A comprehensive study was undertaken to compare neural signals recorded by the EPS with a standard commercial EEG system.
Results
Quantitatively, highly similar signals were observed between the EPS and EEG sensors for both free running and evoked brain activity with cross correlations of higher than 0.9 between the EPS and a standard benchmark EEG system.
Comparison with Existing Method(s)
These studies comprised measurements of both free running EEG and Event Related Potentials (ERPs) from a commercial EEG system and EPS.
Conclusions
The EPS provides a promising alternative with many added benefits compared to standard EEG sensors, including reduced setup time and elimination of sensor cross-coupling. In the future the scalability of the EPS will allow the implementation of a whole head ultra-dense EPS array.
For more information, please click here >>

 Read more
Read more.jpg)




